Resource Management Glossary: Key Terms
Definition of Project portfolio management
What is project portfolio management?
Project portfolio management (PPM) is the strategic process of selecting, prioritizing, and managing an organization's projects as a unified portfolio rather than as isolated efforts. The goal is to align all initiatives with business objectives, optimize resource allocation, and maximize overall value.
Unlike traditional project management, which focuses on delivering a single project successfully, PPM looks at the bigger picture, balancing competing priorities, mitigating risks, and ensuring the right mix of projects are executed at the right time.
PPM gives decision-makers a complete view of performance, dependencies, and ROI across the entire portfolio, enabling smarter and faster strategic choices.
How can project portfolio management benefit an organization?
A well-implemented PPM framework provides both operational control and strategic agility. Key benefits include:
- Strategic alignment – Ensures that every project supports company-wide goals.
- Better resource allocation – Assigns people, budget, and tools to the projects with the highest impact.
- Risk reduction – Identifies risks early across the portfolio, allowing preventative action.
- Improved decision-making – Provides leadership with real-time data for investment and prioritization.
- Higher ROI – Focuses on initiatives that promise the greatest value relative to cost.
- Portfolio visibility – Creates transparency into status, deadlines, dependencies, and blockers.
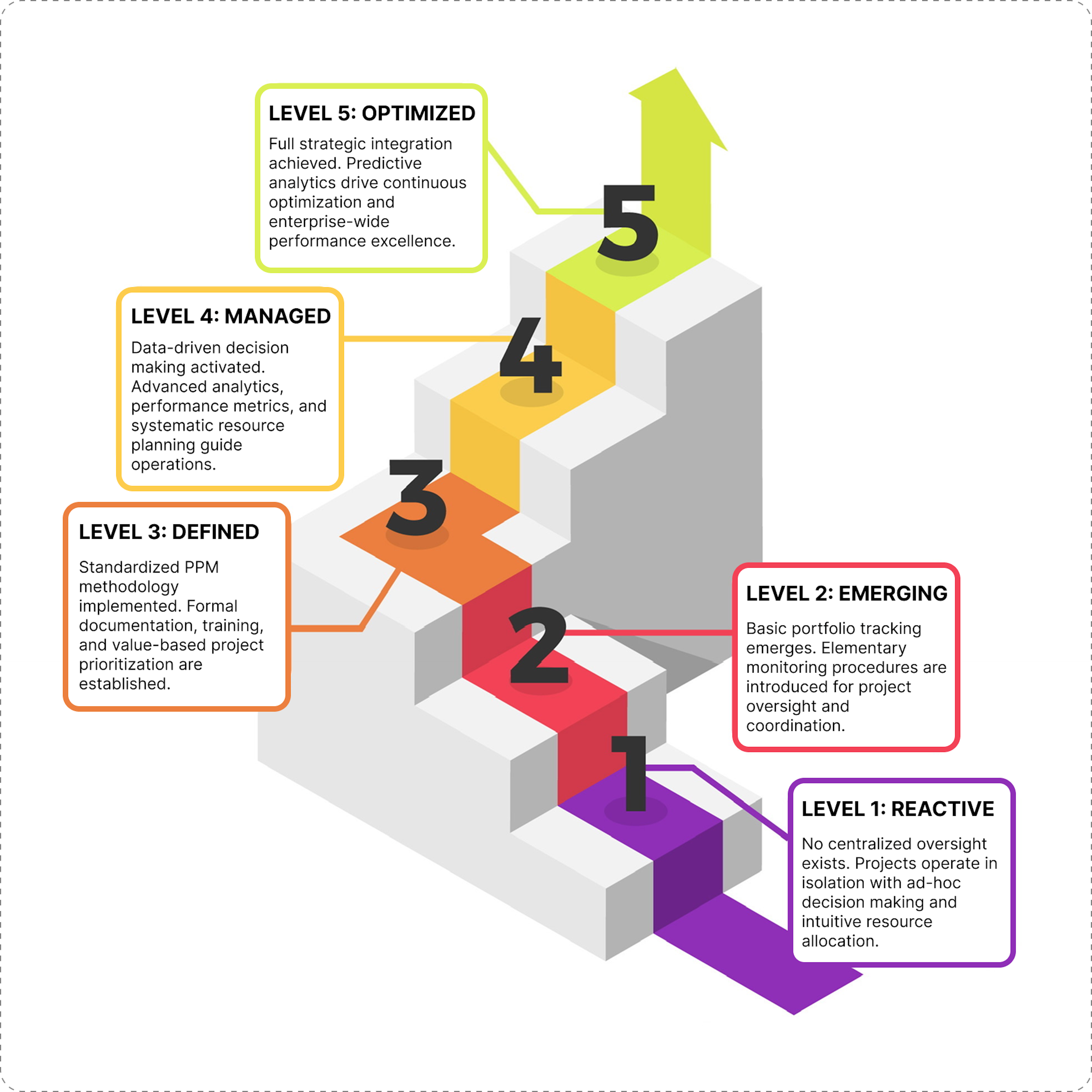
What are the 5 levels of PPM?
Organizations mature in PPM through five progressive levels:
- Reactive – Projects are handled individually with no portfolio oversight; priorities shift ad hoc.
- Emerging – Basic portfolio tracking begins, but without unified processes or strategy alignment.
- Defined – Standardized PPM processes are in place; projects are clearly linked to business goals.
- Managed – Advanced reporting, capacity planning, and prioritization govern portfolio decisions.
- Optimized – PPM is fully integrated with strategy, using predictive analytics and continuous improvement to maximize outcomes.
Moving up these levels means increasing control, foresight, and value extraction from the project portfolio.
What are the keys to successful project portfolio management? How to implement PPM?
Success in PPM is all about governance and discipline, far beyond a simple software.
Keys to success:
- Clear strategic objectives – Define what success looks like for the portfolio as a whole.
- Strong governance – Establish a portfolio board or decision-making body.
- Transparent prioritization criteria – Projects ranked based on ROI, risk, and strategic fit.
- Cross-functional collaboration – Ensure departments are aligned on resource sharing and priorities.
- Accurate, timely data – Base decisions on real performance metrics.
Implementation steps:
- Assess current maturity – Determine where you stand on the 5 PPM levels.
- Design the governance framework – Assign roles, responsibilities, and decision rights.
- Select the right tools – Choose PPM platforms that integrate with your workflows.
- Roll out in phases – Pilot with a subset of projects before full implementation.
- Train and communicate – Ensure teams understand PPM's value and processes.
- Review and adapt – Use metrics to refine portfolio processes continuously.
Organizations often struggle when jumping straight into tooling without aligning culture, governance, and data visibility first.
What are project portfolio management tools?
PPM tools are specialized platforms that consolidate project data, track portfolio performance, and assist with resource planning, prioritization, and reporting. They give leaders a real-time command center for portfolio oversight.
Core capabilities of modern PPM tools include:
- Centralized project tracking and dashboards
- Resource and capacity management
- Goal alignment and KPI monitoring
- Risk and dependency visualization
- Financial tracking and ROI analysis
How can Enji be used as a PPM tool?
While Enji is widely adopted in software engineering performance management, its integrated metrics dashboards and operational insights make it a strong companion for PPM, especially in tech-driven organizations.
PPM-supporting features in Enji:
- Agile metrics dashboard – Track delivery performance KPIs (lead time, cycle time, estimation accuracy) across all active projects.
- Portfolio-level KPIs – Use aggregated views to assess progress, bottlenecks, and outcomes across multiple projects.
- Financial metrics dashboard – Analyze project margins, time/resource costs, and employee profitability with transparent, real-time data—enabling smarter budgeting, pricing, and long-term strategic planning.
- Enlightening worklogs – Understand real resource allocation and availability before approving new initiatives.
- SOW planning – Balance workloads to prevent overcommitment and ensure priority projects stay on track.
- Automated alerts – Detected when metrics trend toward risk, enabling proactive intervention.
- Retrospective-ready reports – Feed lessons learned back into portfolio-level strategic decisions.
Example: A PMO overseeing five strategic software projects uses Enji's aggregated delivery metrics to compare lead times and rejection rates across initiatives. Projects lagging behind portfolio benchmarks are flagged early, and resources are redistributed within a week—avoiding cascading delays.
Key Takeaways
- PPM is the coordinated management of multiple projects to align with strategy, optimize resources, and maximize portfolio value.
- Benefits include strategic alignment, improved ROI, reduced risk, and higher resource efficiency.
- The 5 levels of PPM maturity move from reactive to fully optimized, predictive portfolio management.
- Successful implementation requires clear objectives, governance, prioritization, collaboration, and quality data.
- PPM tools centralize portfolio oversight; Enji enhances this by providing real-time delivery, capacity, and performance insights that lead to faster, data-driven decisions.
Last updated in August 2025